Securing Your Cyberspace: Laws and Best Practices to Combat Online Scams.

The internet has become an integral part of our daily lives. From shopping online to connecting with friends and colleagues, the World Wide Web has made our lives more convenient than ever before. However, with great opportunities comes great trouble, as the online world is also teeming with scams and cybercrime.
Contents
- What is an Online Scam?
- How to protect yourself from Online scams?
- 1. Don’t click on unknown links.
- 2. Be careful of who you buy from.
-
- 3. Never give out your personal details.
- 1. Consumer Protection Act 2019
- 2. Information Technology Act of 2000
- a. Section 43 - Unauthorized Data Access:
- b. Section 66 - Punishing Phishing:
- c. Section 66A - False Information Spreading:
- d. Section 66C - Unauthorized Use of Passwords:
- e. Section 66D - Impersonation:
- 3. Indian Penal Code of 1860
- b. Criminal Breach of Trust (Sections 405 and 406):
- c. Cheating (Sections 415 - 419):
- d. Mischief (Sections 425 and 426):
- e. Forgery (Sections 463 – 465, 467-477):
- How to Report a Scam?
- Wrapping Up
What is an Online Scam?
Online scams are deceptive and fraudulent activities carried out on the internet to steal your money, personal information or both.
The scams come in various forms,
Phishing emails.
Fake websites.
Online shopping frauds.
Advance-fee frauds.
Identity theft, to name a few.
In the past two years alone,75% of the cyber crimes in India were financial scams. These scammers are skilled at manipulating unsuspecting individuals into believing their deceptive schemes, often leading to financial and emotional distress.
With the wider acceptance of e-commerce platforms, fake shopping sites and marketplaces take centre stage in online scamming. Studies suggest that by 2023, $48 billion will be lost through online payment scams on fake shopping sites.
Also read The Rising Threat of Ticket Scams: What You Should Look Out For?
How to protect yourself from Online scams?
It may seem impossible but there are tried and tested ways that you can use to protect yourself from online fraud.
1. Don’t click on unknown links.
The primary step towards safety in the online world is to avoid messages or emails that carry links you don’t know the source of. Such links may be redirected to a banking page or a payment gateway which may look authentic but won’t be. Once clicked, they can track your movements and even extract personal information without your knowledge.
2. Be careful of who you buy from.
There are 12-20 million online marketplaces today. And each has its own policies against counterfeiters and other scammers. But it's not without loopholes. So check who you are buying from, their authenticity, the customer reviews, their product lineup, the location and even their company website. Only proceed if they look credible.
3. Never give out your personal details.
The number one form of online fraud is phishing. Through phishing a scammer manipulates you into sharing your personal, often banking information. So stay away from such calls or messages and if someone asks for your bank account details, immediately drop the call and contact your bank and report the incident.
However, if you get trapped in a scam or are already a victim of fraud, you can always move forward legally and get back what you lost. The Government of India and legal authorities have implemented several laws and regulations to provide legal protection to consumers.
Let's explore three important laws that can help safeguard your online presence and financial well-being.
1. Consumer Protection Act 2019
The fundamental rights of a consumer. The Consumer Protection Act 2019 serves as a robust defence for consumers against scams and fraudulent practices in the marketplaces, both online and offline. This act empowers consumers by:
a. Right to Information: Consumers have the right to access transparent information regarding the products or services they are purchasing. Ensuring that consumers are not misled by false advertising or deceptive claims.
b. Right to Safety: The act ensures that products and services must meet specific safety standards, reducing the risk of harm or financial loss due to substandard goods or services.
c. Right to Redressal: If a consumer falls victim to a scam or receives faulty products, they have the right to seek redressal through a quick and efficient dispute resolution mechanism.
d. Right to Compensation: Victims of online scams can claim compensation for any loss or damage incurred due to deceptive practices.
e. Right to Education: The act emphasizes the importance of consumer education, helping individuals make informed decisions and protect themselves from online scams.
2. Information Technology Act of 2000
With the advancement in technology, the Government of India devised the IT Act, of 2000. The Information Technology Act of 2000 is a comprehensive piece of legislation that ensures the safety and security of consumers in the digital world. It consists of five major sections that protect against various forms of online fraud:
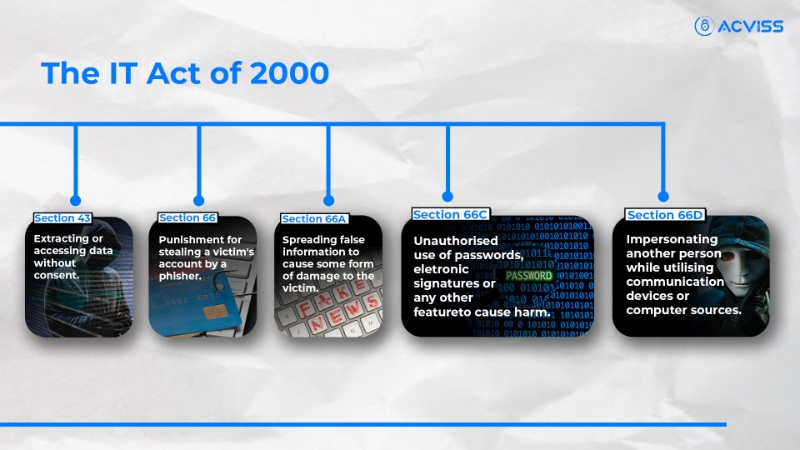
a. Section 43 - Unauthorized Data Access:
This section penalizes anyone who extracts or accesses data without consent, safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access.
b. Section 66 - Punishing Phishing:
Online scammers who steal a victim's account through phishing attacks can face severe penalties under this section, discouraging such fraudulent activities.
c. Section 66A - False Information Spreading:
Spreading false information to cause harm to others is a punishable offence under this section, deterring individuals from engaging in online slander and scams.
d. Section 66C - Unauthorized Use of Passwords:
Anyone who misuses passwords, electronic signatures or other features to cause harm can be prosecuted under this section, strengthening online security.
e. Section 66D - Impersonation:
Impersonating another person while using communication devices or computer sources is prohibited, protecting individuals from identity theft and fraudulent impersonation.
3. Indian Penal Code of 1860
The Indian Penal Code of 1860 also known as the cornerstone of Indian law, extends legal support to scams and crimes committed both online and offline.
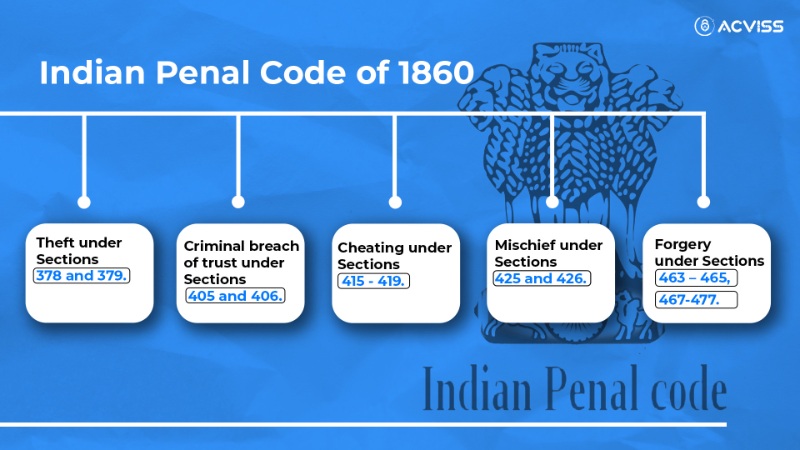
- Theft (Sections 378 and 379): They cover theft and punishment for stealing, ensuring that theft in the digital realm is treated with the same gravity as physical theft.
- Criminal Breach of Trust (Sections 405 and 406): These sections penalize individuals who breach trust or commit fraud, crucial in online scams involving trust violations.
- Cheating (Sections 415 - 419): Anyone found cheating or deceiving others online can face legal consequences under these sections, protecting innocent victims.
- Mischief (Sections 425 and 426): Mischief-related sections prevent online vandals from causing harm or damage to digital assets.
- Forgery (Sections 463 – 465, 467-477): Forgery is taken seriously under the IPC, ensuring that those who falsify documents or identities online are held accountable.

How to Report a Scam?
Knowing your rights and the relevant laws is essential, but reporting a scam is equally crucial. To report an online scam, get in touch with the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal - 1930 or go to their website. https://cybercrime.gov.in
This ensures that law enforcement agencies can take action immediately and protect potential victims. Reporting a scam not only helps you but also contributes to making the internet safer for everyone.
Wrapping Up
The cyber-world is a vast and dynamic space, but it's not without its dangers. Remember that knowledge is your best defence against online scams. Be on the lookout, stay informed and report any suspicious activity promptly. By doing so, you are not only protecting yourself but also contributing to a safer online environment for everyone.
If you're keen to learn more about scams and frauds in both online and offline marketplaces, Truviss is here to help. As a leader in the fight against counterfeits, we'd love to connect with like-minded individuals passionate about this cause.