Digital Product Passport as a Regulatory Requirement: How Brands Will be Affected

Sustainability is a big thing now. Consumers are more aware and environmentally conscious than just price-conscious. Manufacturing processes involving harm to the environment are no longer acceptable in today's eco-conscious world. Consumers demand transparency, and regulators like the European Union (EU) are stepping up with stricter regulations to address environmental concerns.
The EU has been implementing measures to fight deforestation, reduce waste, and promote sustainability. First came theEuropean Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) in 2023, mandating deforestation-free supply chains for commodities like coffee, cocoa, and leather. Now, the EU is taking things a step further by introducing the Digital Product Passport (DPP) under the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR).
The DPP represents a groundbreaking shift in how products are monitored, tracked, and managed throughout their lifecycle. It is not just about ensuring regulatory compliance; it's about creating a comprehensive digital record that tells the story of a product—its origins, composition, and sustainability credentials—all while supporting the EU's ambitious climate goals.
For businesses, particularly those operating in highly regulated markets like the EU, the DPP is more than a compliance requirement. It's a game-changer. This innovative regulation is designed to improve supply chain traceability, encourage responsible production practices, and empower consumers with information to make sustainable choices.
Brands must prepare to embrace this new wave of regulation or risk falling behind. In this blog, we'll explore the ins and outs of the Digital Product Passport, why it matters, and how businesses can navigate this regulatory landscape with confidence.
What is the Digital Product Passport (DPP)?

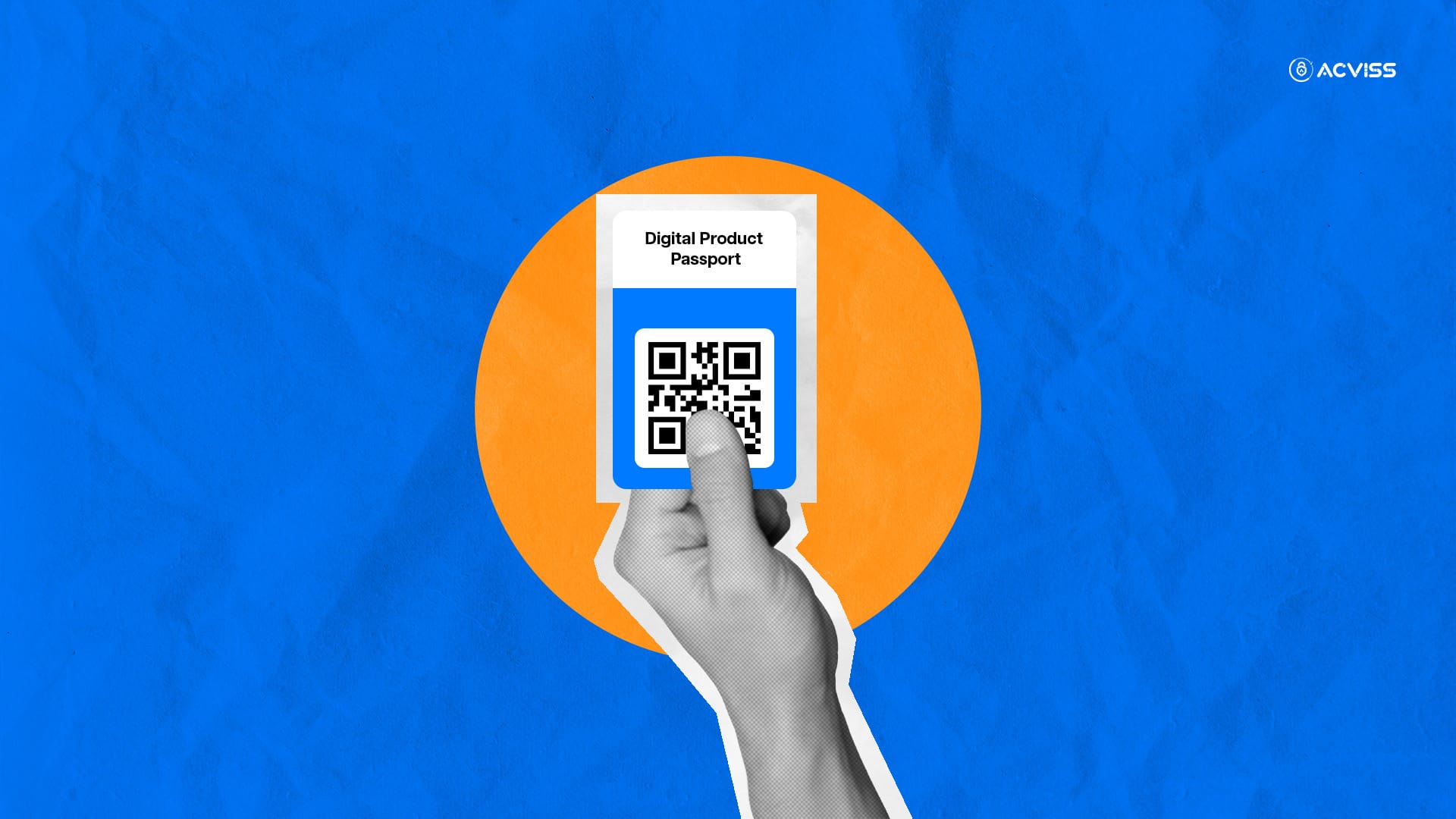
Digital Product Passport (DPP) is a comprehensive digital record of a product's lifecycle designed to enhance transparency, accountability, and sustainability across the supply chain. It is a digital file attached to every product you manufacture or purchase that contains its entire story, from its origin to how it can be recycled at the end of its life.
DPP was introduced as part of the EU's Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR) and supports the EU's mission to transition to a circular economy. It acts as a one-stop repository of essential information for stakeholders. From manufacturers to consumers, everyone can access this information to make informed decisions.
1. Functionality: How Does the DPP Work?
The DPP is a data-driven tool that streamlines supply chain traceability, product authentication, and compliance tracking. Its primary aim is to ensure that products entering the EU market meet the highest standards of sustainability and ethical production. Here's how it works:
- Data Centralisation: The DPP consolidates critical product data in a single digital location, accessible via technologies like QR codes or RFID tags.
- Real-Time Updates: This allows for real-time updates throughout the supply chain, ensuring that information remains accurate and up-to-date.
- Accessible for All: From manufacturers and retailers to consumers and regulators, everyone in the product life cycle chain can access the DPP to verify regulatory compliance or learn more about the product.
2. Core Elements of the DPP
The DPP isn't just a generic record; it's a treasure trove of vital product information. Some of the key data points it covers include:
- Material Sourcing: Details about where the raw materials were sourced, ensuring they comply with regulations like the EUDR.
- Carbon Footprint: The environmental impact of producing, transporting, and using the product.
- Composition: A breakdown of the materials and chemicals used, ensuring they meet safety and sustainability standards.
- Recycling Instructions: Guidance on how the product or its components can be recycled, promoting circularity.
- Certifications and RegulatoryCompliance: Proof of adherence to regulatory requirements such as sustainability certifications or deforestation-free sourcing.
- End-of-Life Options: Clear steps for disposing of or repurposing the product at the end of its lifecycle.
3. The Role of DPP in Product Lifecycle Management
DPP is the ultimate transparency tool. It provides a detailed record of a product's journey, from raw material to disposal, and empowers brands to:
- Build Trust: Consumers can make confident purchases, knowing they're buying ethically produced and environmentally responsible goods.
- Meet Regulatory Standards: Businesses can streamline compliance with stringent EU regulations, avoiding penalties and gaining a competitive edge.
- Encourage Sustainability: The DPP fosters a culture of responsible production and consumption, contributing to the EU's broader climate goals.
Why the Digital Product Passport Matters

The Digital Product Passport (DPP) is more than just a regulatory requirement; it's a transformative tool that shapes how businesses operate in a rapidly evolving market. Here is how DPP impacts brands, consumers, and the environment.
1. Reducing Environmental Impacts
DPP is designed to drive sustainability by addressing some of the most pressing environmental challenges.
- Combatting Waste
- Promoting Responsible Sourcing
- Lowering Carbon Footprints
2. Strengthening Supply Chain Transparency
The DPP revolutionises supply chain management by fostering trust and accountability across every touchpoint.
- Traceability Made Easy: It provides a bird's-eye view of the entire supply chain, from raw materials to the final product.
- Eliminating Grey Areas: Counterfeit goods and unethical practices often thrive in opaque systems. The DPP shines a light on every stage of production, reducing these risks.
- Enhanced Consumer Trust: When consumers know exactly where a product comes from and how it's made, they are more likely to trust and support the brand.
3. Helping Businesses Align with EU Sustainability Goals
The EU's ambitious climate goals are at the heart of regulations like the DPP.
- Circular Economy Push
- Boosting Brand Credibility
- Market Expansion
4. The Cost of Non-Compliance
While the benefits of the DPP are substantial, the consequences of non-compliance can be equally severe:
- Financial Penalties: Non-compliance could result in hefty fines, reaching up to €20 million or 4% of the company's global turnover.
- Regulatory Warnings: Businesses may receive official reprimands for failing to meet compliance standards.
- Operational Bans: Companies could face temporary or permanent restrictions on certain business operations.
- Legal Consequences: Severe violations may lead to criminal charges.
- Loss of Competitiveness: Non-compliance can drive customers toward environmentally responsible competitors, leading to reduced market share.
- Erosion of Brand Trust: Failing to align with regulations can damage customer loyalty, making it harder to rebuild credibility.
- Stifled Growth: Non-compliance could limit partnerships with sustainability-focused businesses, restricting expansion opportunities.
This was a small glimpse of why DPP matters. The sooner businesses adapt, the better equipped they will be to thrive in a market increasingly prioritising sustainability and accountability.
Incorporating tools like Origin by Acviss for supply chain traceability can simplify this transition, ensuring regulatory compliance while building trust and credibility.
Products Affected by DPP Requirements
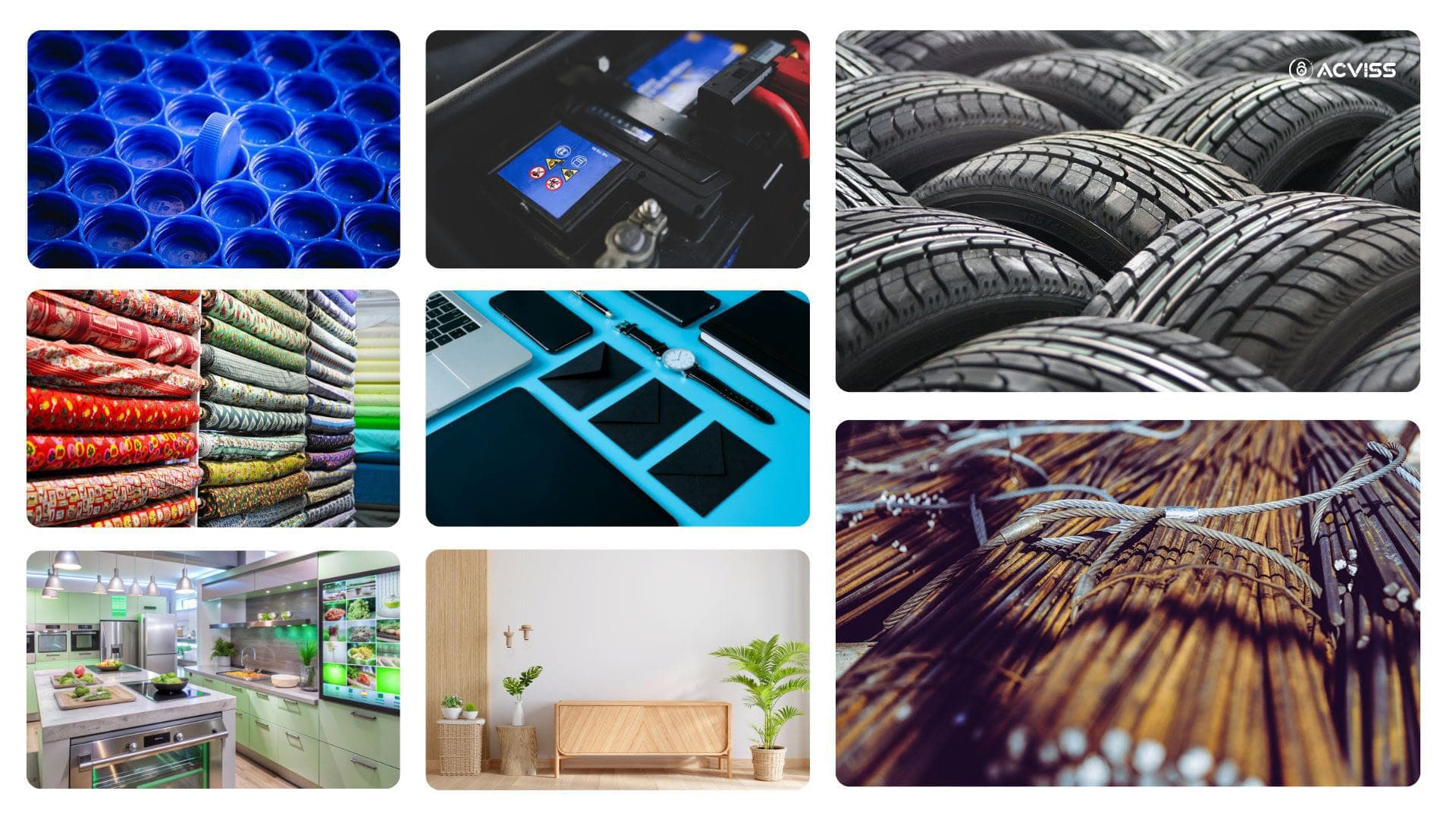

The Digital Product Passport (DPP) is poised to reshape industries by mandating transparency across a wide range of product categories. Here's a detailed look at the key sectors covered and why they are prioritised:
1. Batteries (Industrial and EV)
- Why Included: Batteries are critical to the clean energy transition but have significant environmental concerns tied to resource extraction and disposal.
- Focus Areas: Traceability of raw materials like lithium and cobalt, recycling methods, and overall lifecycle impact.
2. Textiles (Garments and Footwear)
- Why Included: The textile industry is a major contributor to waste and pollution due to its fast fashion model.
- Focus Areas: Fibre sourcing, water usage, chemical treatments, and end-of-life recycling.
3. Electronics and ICT Products
- Why Included: Electronics contribute to e-waste and rely heavily on finite resources.
- Focus Areas: Composition of metals like gold and rare earth elements, energy efficiency, and repairability.
4. Furniture
- Why Included: Furniture production often involves unsustainable logging and synthetic materials that are hard to recycle.
- Focus Areas: Sourcing of wood and other materials, use of harmful chemicals, and disposal options.
5. Construction Materials
- Why Included: This sector has one of the highest environmental footprints due to resource-heavy processes.
- Focus Areas: Sustainable sourcing of raw materials like cement and steel, carbon emissions during production, and recycling potential.
6. Plastics, Chemicals, and Packaging
- Why Included: These materials dominate landfills and marine pollution, demanding urgent attention.
- Focus Areas: Biodegradability, recyclability, and chemical composition.
7. Energy-Related Products (Appliances and Lighting)
- Why Included: These products significantly impact energy consumption and carbon emissions.
- Focus Areas: Energy efficiency ratings, durability, and disposal guidelines.
8. High-Risk Commodities (Tyres and Lubricants)
- Why Included: Tyres contribute to microplastic pollution, and lubricants can harm ecosystems if improperly disposed of.
- Focus Areas: Chemical makeup, recycling processes, and environmental impact during use.
Why These Categories Are Prioritised
These sectors are prioritised due to their high environmental impact, potential for resource depletion, and global regulatory focus. Their inclusion in the DPP ensures:
- Transparent material sourcing.
- Improved recyclability and circularity.
- Enhanced accountability throughout the supply chain.
The DPP is designed to evolve. As industries adapt, additional product categories are likely to be included, expanding the scope to cover emerging sectors and materials with significant environmental footprints. Brands must stay proactive to align with upcoming requirements.
How Brands Will Be Affected by DPP Implementation

The Digital Product Passport (DPP) is more than just a compliance requirement; it's a transformative regulation that will impact brands on multiple levels. Let's explore how:
Operational Impact
Integrating DPP into existing supply chains will require brands to overhaul their processes:
- Data Collection and Management: Companies must ensure the accuracy and accessibility of detailed product information, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life recycling.
- System Integration: Existing supply chain management systems may need upgrades to incorporate DPP-related data seamlessly.
- Training and Awareness: Employees and partners across the supply chain must be educated about the requirements and functionality of the DPP.
Cost Implications
While the long-term benefits of DPP are undeniable, the initial implementation comes with financial challenges:
- Technology Investments: Adopting new tools like blockchain or IoT devices for real-time tracking and data storage.
- Certification Expenses: Costs associated with third-party audits and certifications to validate compliance.
- Administrative Costs: Time and resources spent on documenting processes, collecting data, and maintaining compliance records.
Competitive Edge
Brands that embrace the DPP early stand to gain significant advantages:
- Market Access: Compliance with DPP ensures uninterrupted access to the lucrative EU market.
- Consumer Trust: Transparency builds loyalty as consumers increasingly value ethical and sustainable products.
- Brand Credibility: Early adoption signals leadership in sustainability, giving brands a reputational boost.
Challenges Brands Face with DPP Implementation
The road to DPP compliance is not without hurdles. Here are the key challenges that brands must navigate:
1. Fragmented Supply Chains
- Many supply chains span multiple regions and involve various stakeholders, making it difficult to gather accurate and comprehensive data.
- A lack of centralised systems often leads to data gaps, which can compromise compliance.
2. High Implementation Costs
- Transitioning to DPP compliance requires significant investment in technologies, such as blockchain and process upgrades.
- Smaller businesses may find these costs particularly burdensome, creating barriers to entry into the EU market.
3. Collaboration Challenges
- DPP compliance demands coordinated efforts between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors.
- Misaligned priorities or lack of communication among these parties can delay implementation.
4. Limited Awareness
- Many brands are still unaware of the full scope and implications of DPP requirements.
- A lack of understanding can result in incomplete compliance efforts, risking penalties and reputational harm.
Despite these challenges, proactive planning, collaboration, and the adoption of advanced tools can help brands overcome obstacles and align with the DPP's vision.
Benefits of Adopting Digital Product Passport
The Digital Product Passport (DPP) brings value to brands, consumers, and the environment alike. Here are the benefits of adopting DPP:
For Brands
- Improved Reputation: By providing transparency and adhering to sustainability regulations, brands can position themselves as leaders in ethical production, boosting customer trust.
- Increased Market Access: Compliant brands gain unrestricted access to the EU market, avoiding penalties and maintaining a competitive edge.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: With centralised and real-time data, brands can optimise processes, reduce redundancies, and improve decision-making.
For Consumers
- Transparency: Consumers get detailed insights into a product's sourcing, composition, and environmental footprint, empowering them to make informed choices.
- Confidence in Quality: Products with a DPP assure buyers of ethical and sustainable practices, increasing trust and loyalty.
- Simplified Recycling: Clear end-of-life instructions make recycling and reusing products easier for consumers, fostering a culture of sustainability.
For the Environment
- Reduced Waste: By promoting circular economy principles, the DPP encourages recycling and efficient resource utilisation, minimising waste.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Transparency drives accountability, compelling brands to adopt greener practices.
- Sustainability Advocacy: The DPP's implementation sets a precedent for global sustainability efforts, amplifying its positive environmental impact.
Strategies for DPP Regulatory Compliances
Meeting DPP requirements can seem daunting, but with the right strategies, brands can achieve this regulatory landscape effectively:
1. Data Collection and Traceability
- Importance of Data: Accurate lifecycle data ensures compliance and builds consumer trust.
- Track and Trace Systems: Implement solutions like Origin by Acviss, which offers real-time visibility across supply chains.
- Blockchain Integration: Use blockchain to create an immutable record of sourcing, manufacturing, and distribution activities.
2. Technological Solutions
- IoT (Internet of Things): Smart sensors can monitor supply chain activities in real-time, ensuring accurate data collection.
- Automation: Automate data input and compliance checks to reduce manual errors and save time.
3. Partnerships and Collaboration
- Work closely with distributors and suppliers to make sure all links in the supply chain meet DPP standards.
- Share knowledge and resources with stakeholders to foster a collaborative approach to compliance.
Steps to Prepare for DPP Compliance
Preparation is key to adopting the complexities of DPP implementation. Here are actionable steps to get started:
1. Conduct Supply Chain Audits
- Assess your current supply chain operations to identify gaps in data, traceability, and compliance.
- Use the audit findings to create a roadmap to align with DPP requirements.
2. Invest in Technology
- Adopt traceability solutions like Acviss's Origin to track and verify product lifecycle data.
- Explore tools like blockchain and IoT for accurate and efficient data management.
3. Collaborate Across the Supply Chain
- Engage with suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to align processes and ensure data consistency.
- Create partnerships with third-party certification bodies for compliance validation.
4. Train Teams on DPP Requirements
- Educate employees about the importance of the DPP and how it aligns with sustainability goals.
- Provide training on using new technologies and adhering to regulatory standards.
By taking these proactive steps, brands can ensure compliance as well as gain a competitive advantage in the evolving regulatory landscape.
How Origin by Acviss Can Support Brands
The Digital Product Passport (DPP) demands meticulous tracking and transparency, and that's whereOrigin by Acviss shines. As a cutting-edge supply chain traceability platform, Origin equips brands with the tools to meet DPP requirements effortlessly while enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Features of Origin by Acviss
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: Track your product's journey across the supply chain with instant, up-to-date information. This ensures you're always aware of sourcing, manufacturing, and distribution activities.
- Blockchain-Powered Records: Origin leverages blockchain technology to create tamper-proof, immutable records of your product lifecycle. This feature guarantees transparency and builds trust among consumers and regulators alike.
- Seamless Integration: Whether your supply chain systems are advanced or basic, Origin is designed to integrate smoothly, making compliance a hassle-free process.
Benefits for Brands
- Regulatory Compliance Made Easy: Origin simplifies adherence to DPP requirements by consolidating data in one accessible, secure system.
- Cost Savings: Automated data collection and tracking reduce manual effort, cutting down on operational costs.
- Enhanced Consumer Trust: Transparency in product lifecycle details builds credibility and loyalty among eco-conscious consumers.
- Competitive Edge: By adopting Origin, brands position themselves as sustainability leaders in a market increasingly driven by responsible practices.
Conclusion
The Digital Product Passport (DPP) is a transformative step toward a more transparent, sustainable, and consumer-focused world. For businesses, it's a chance to take charge of shaping the future of sustainability.
By embracing the DPP, brands can turn challenges into opportunities: building stronger consumer relationships, gaining competitive advantages, and contributing to the global push for environmental responsibility. It's not just about ticking regulatory boxes; it's about creating a legacy of trust and innovation. For brands ready to step into this new era, the time to act is now. Get in touch with today and make the transition smoother, secure your supply chain and empowering businesses to not only comply but excel.
