The Top Counterfeit Products in Every Major Industry
Did you know counterfeit products cost the world economy more than $500 billion annually? This shocking statistic by the US Chamber of Commerce brings our attention to an unnoticed but rising issue that impacts organisations, customers, and even authorities worldwide. Counterfeiting is more than simply an imitation of luxury handbags or gadgets; it is a crime that jeopardises public safety, helps organised crime, and deprives cities of critical tax income.
The US Department of Commerce says that counterfeit items cause more than 70 fatalities and 350,000 injuries every year. In this blog, we will discuss the widespread implications of counterfeiting, the sectors most affected, and how sophisticated technology has made counterfeit items more convincing—and dangerous—than ever before.
The Scope of Counterfeit Products Across Industries
Fake products have become a multibillion-dollar global business affecting every industry. The development of globalisation and technical improvements has made counterfeiting simpler, more complex, and difficult to detect.
Here's why counterfeiting is a concern for everyone:
- Consumer Safety Risks: Fake items often originate from subpar, hazardous materials, posing major health and safety risks.
- Identity Theft and Fraud:Phishing websites that offer imitations may steal your confidential and financial data or harm your gadgets with malware.
- Economic Impact: Counterfeiters do not pay taxes, leaving communities without finances for schools, hospitals, and other services. This unfair rivalry also compromises legal companies, especially small ones, resulting in job losses and increased consumer costs.
- Organised Crime Support: Profits from counterfeit products are frequently used to support illicit activities such as drug trafficking and terrorism.
- Ethical Issues: Many copycat companies employ forced or underage labour, exploit workers, and operate in hazardous settings.
- 3D Printing and Imaging Technology: High-resolution printers and specialised inks can now copy labels, holograms, and even security features with near-perfect precision.
- Chemical and Material Replication: Advanced chemistry enables fraudsters to duplicate the intrinsic qualities of real items, rendering them nearly identical.
- Digital platforms: False sellers can use social media and bogus e-commerce websites to create professional-looking shopfronts, expanding their audience and enticing more naive consumers.
With these improvements, spotting fake products has become more challenging for buyers and corporations.
Top Counterfeited Products by Industry
Fake goods have become a worldwide concern, threatening consumer security, company credibility, and financial stability. Below are various sectors combating the counterfeit epidemic:
A. Pharmaceuticals

Counterfeit drugs are becoming a major global threat, with incidences increasing from 196 in 2002 to roughly 6,900 by 2023, according to the Pharmaceutical Security Institute. Fake medicines, vaccinations, and lifestyle medications are frequently available without a prescription. But which medications are most vulnerable?
Examples include:
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- HIV/AIDS
- Malaria
- Antibiotics
- Pain killers
- Central nervous system medicines.
The majority of these counterfeit pharmaceuticals are manufactured in China and India, with main transit ports in Singapore and the UAE, according to the Trade in Counterfeit Pharmaceutical Products report. Counterfeit medicinal products worth Rs. 2 crores from well-known brands such as Sun Pharma, Cipla, and GSK were seized in Kolkata. This demonstrates the rising magnitude and necessity of combating counterfeit pharmaceuticals.
B. Automobiles
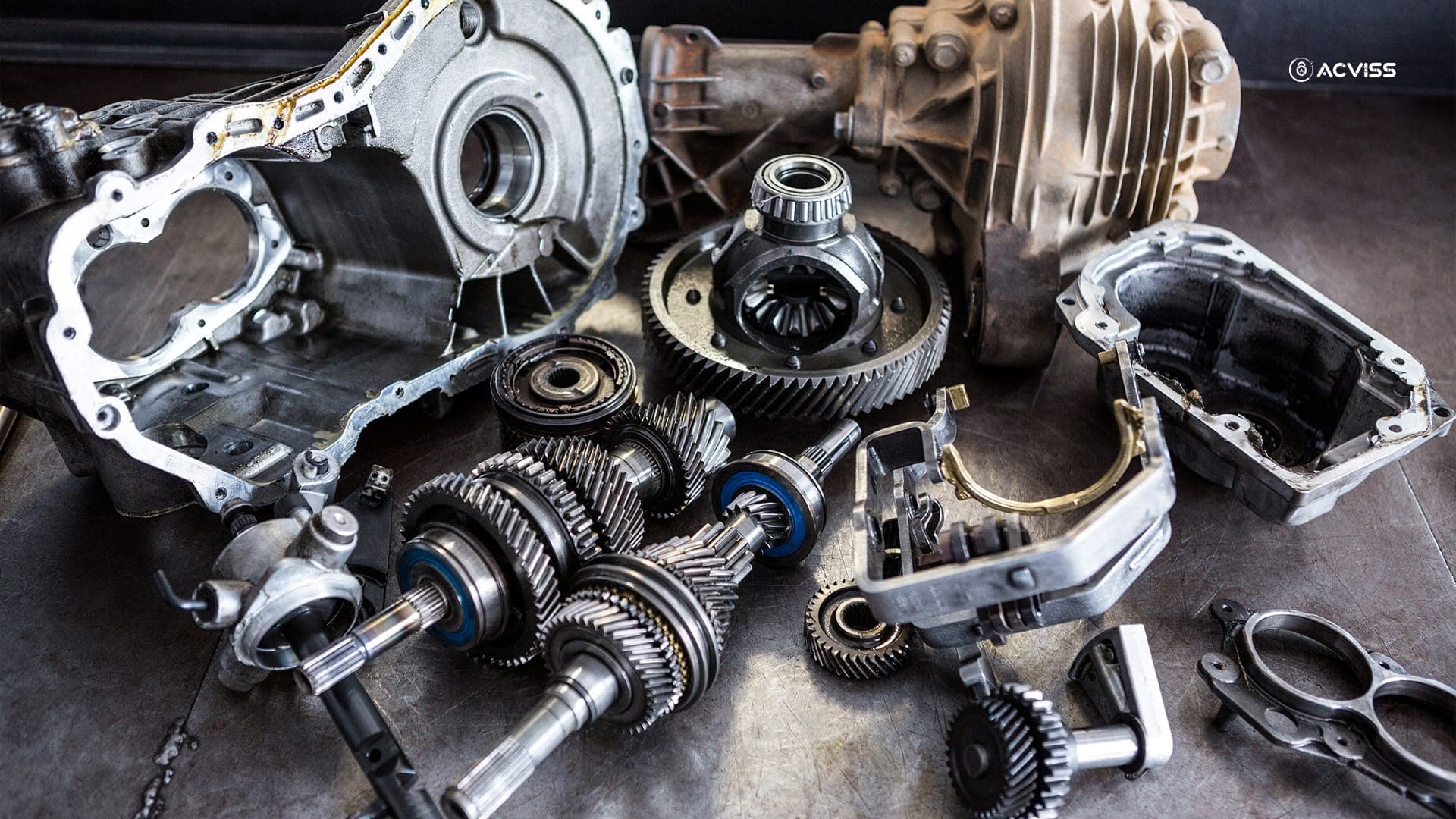
Purchasing imitation auto parts might seem to be a cheap solution, but the consequences are far more costly. Fake components have a significant influence on both vehicle safety and performance. So, which parts are the most typically counterfeited?
- Airbags
- Brake pads
- Engine components
- Windscreens
- Wheels
Consequences for automakers:
- Increased warranty claims owing to faulty parts.
- Customer unhappiness as bogus components leads to poor performance, destroying faith in the brand.
China, identified as a major supplier of worldwide trafficked fraudulent auto parts since its automobile market expansion in the mid-1990s.
In October 2024, a TF1 broadcast showed the confiscation of over 80,000 counterfeit automobile components in Marseille mislabelled as Renault and Stellantis, revealing a significant problem related to illegal companies in Turkey.
Read also : The Role of Third-Party Inspection Services in Ensuring Auto Parts Authenticity
C. Electronics

The fraudulent electronics sector is rapidly expanding. These counterfeit items not only deceive consumers, but also pose major dangers to safety, data security, and industry confidence.
Most prevalent counterfeit electronics:
- Smartphones and tablets: Big-name products are frequently duplicated using low-cost materials, resulting in low efficiency, overheating, and even security issues.
- Duplicate Components: Fake parts including integrated circuits, capacitors, and connectors can cause system failures, short circuits, and explosions.
- Accessories: Batteries, chargers, and cords may look real, but they could spark or damage your gadget.
- Pirated Software: Using unauthorised applications raises the danger of infection, cyber assaults, and data breaches.
- Wearables and Electronics: Fake smartwatches, fitness trackers, and headphones frequently fail to operate smoothly.
Wondering how do these counterfeits get into the market? Global component shortages and increasing demand make it simpler for counterfeiters to game the system. Furthermore, complex forgeries are difficult to detect, and uncontrolled vendors in particular locations take advantage of lax intellectual property rules.
Global hub of fake electronic goods:
China is the world's leading manufacturer of fake gadgets and electrical equipment, with Hong Kong acting as the major transit hub, while other manufacturers such as India, Thailand, and Mexico target regional markets via a variety of transportation methods, including sea, air, and postal service.
Real-life incident:
Xiaomi had almost 9,000 counterfeit items seized in 2022, up from 3,000 in 2020, which is proof that this issue is rapidly growing.
D. Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG)
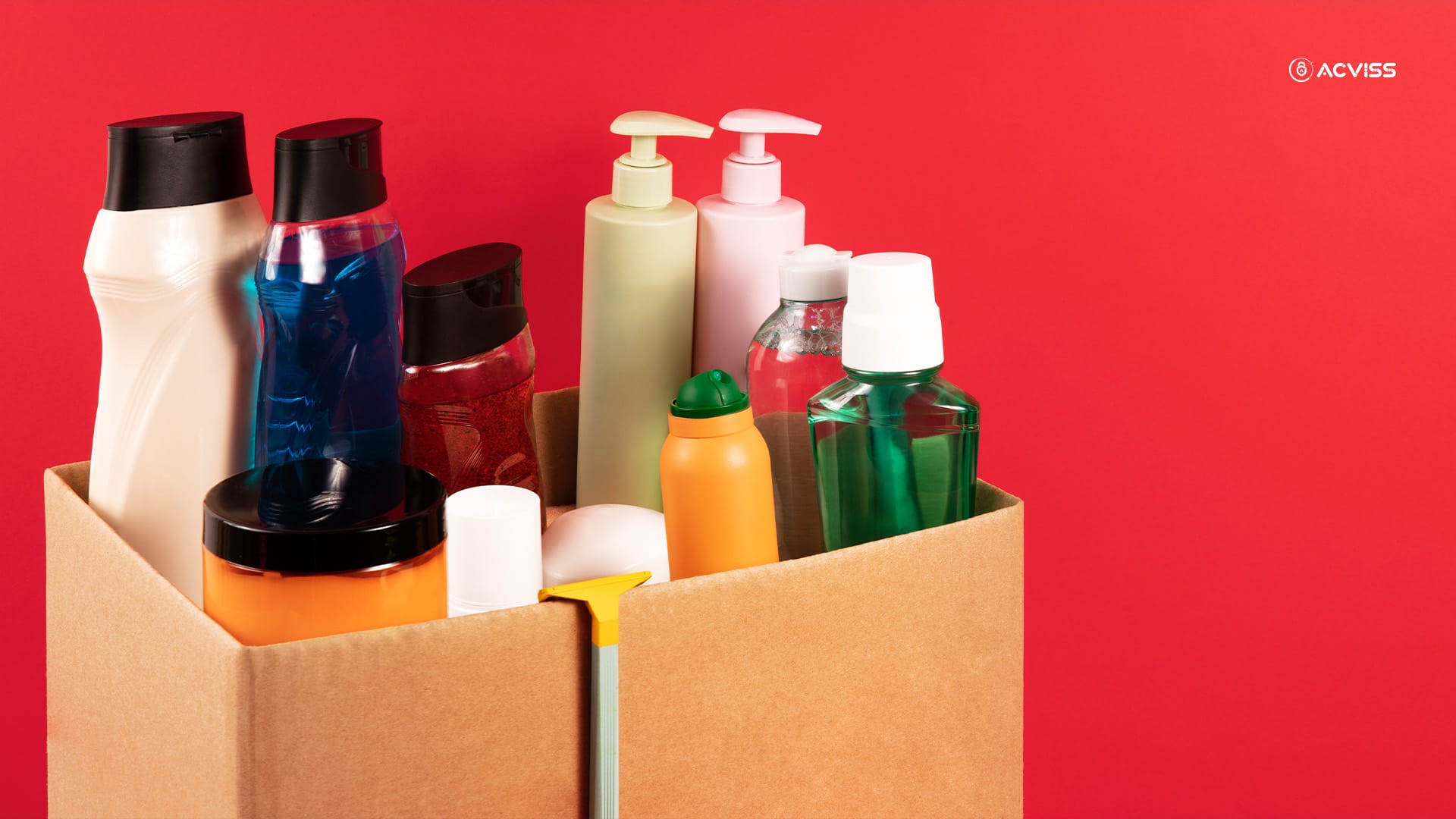

Duplicate retail items, such as cosmetics, toiletries, and food products, are growing increasingly common globally. These counterfeit items pose major health concerns and erode brand trust, impacting customers and companies alike. Let's take a look at some typical counterfeit things.
Personal Care:
- Fake makeup, such as foundations, lipsticks, and mascaras, often imitate high-end items.
- Imitation of skincare goods, such as serums and moisturisers, may cause skin irritation.
- Shampoos and conditioners are typical instances of phoney goods.
Food Products:
- Olive oil: blended with cheaper oils such as sunflower oil, as evidenced in the "Operacion Cholesterol" case from 2006.
- Seafood: Species substitution, such as tilapia sold as red snapper, might result in allergic responses.
- Honey: Contaminated with glucose or corn syrup, lowering purity.
- Maple Syrup: Contains high fructose corn syrup, which raises health risks.
- Dairy Products: Fake cheese and diluted milk can lead to nutritional deficits.
- Whey Protein: Frequently mixed with cheaper proteins, causing stomach difficulties.
- Spices: Using a resemblance to saffron, cinnamon, or pepper may be detrimental to both taste and health.
- Organic Foods: False branding deceives customers and exposes them to pesticides.
- Coffee: Frequently mixed with additives like chicory, which can cause allergic responses.
- Wine: About 20 per cent of all wines sold globally are imitations, with some containing fatal methanol.
This has major medical consequences. Health problems and organ damage could result, as can massive economic losses. China, Southeast Asia, and portions of Europe are key counterfeit production hubs, with Chinese officials seizing $120 million in fake cosmetics in 2017.
E. Luxury Goods
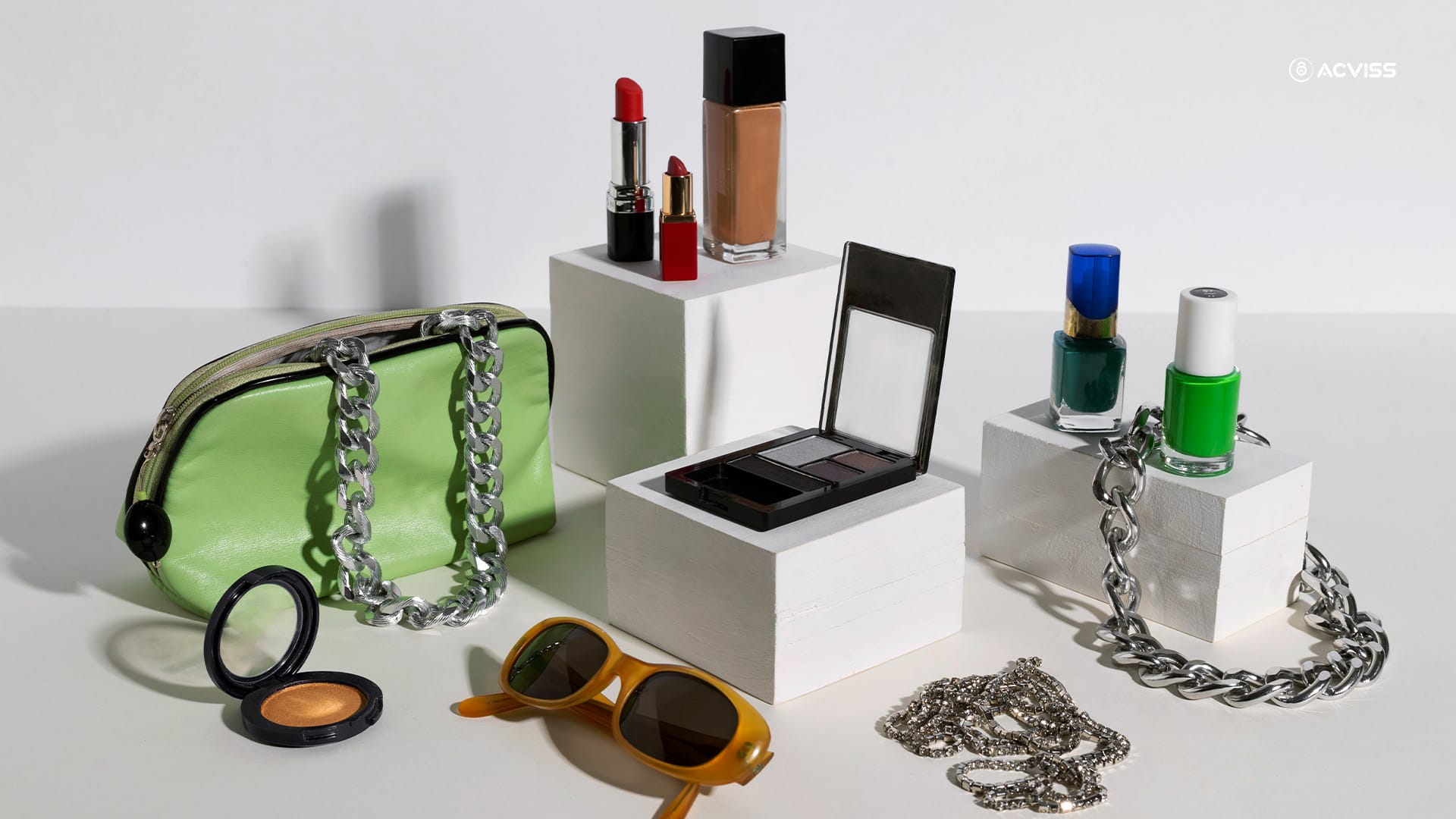

High-end things like handbags, watches, perfumes, and clothing have traditionally served as status symbols. However, as e-commerce sites gain popularity, copycat premium products flood the market, hurting elite companies' reputations. Fake items not only mislead clients but also create parallel markets, jeopardising the financial stability of authentic upscale companies.
So, where are the imitations most common?
- Online Marketplaces: Outlets like eBay, Amazon, and Alibaba have emerged as major hubs for mimicking expensive items, allowing fraudsters to quickly reach global buyers.
- Economic Losses: Each year, faking loses the fashion industry billions of dollars.
Counterfeit hotspots include:
- China's Anfu Market is well-known for producing high-quality copies.
- Palika Bazaar, New Delhi, is a notable counterfeiting hotspot in India.
- Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, and Thailand are regular targets for luxury labels such as Gucci, Louis Vuitton, and Prada.
Counterfeiting causes long-term damage to upscale businesses and misleads customers into purchasing inferior items. Combating this needs coordination among businesses, authorities, and internet platforms.
The Hidden Costs of Counterfeiting
Counterfeiting may appear unconcerned yet its implications are broad and severely devastating. It has an impact on businesses, customers, and the economy that most people are unaware of. Let us break it down.
1. Economic Impact
- Rising Litigation Costs: Defending intellectual property is not affordable. Companies spend millions of dollars combating fraudsters in protracted legal fights.
- Lost Tax Revenue: Governments also lose money since imitation goods frequently avoid taxes and tariffs, resulting in a significant deficit in public funding.
2. Health and Safety Concerns
- Consumer harm: Counterfeit items may be detrimental in areas such as medications, appliances, and transportation. According to the WHO, fraudulent drugs caused more than 100,000 deaths in 2019 alone.
- Environmental Damage: The use of cheap supplies in replicas contributes to pollution and waste, whereas real companies adhere to ethical regulations.
3. Brand Reputation Damage
- Customer Trust Deterioration: Poor-quality imitations leave buyers disappointed, and unfavourable evaluations may ruin even the most powerful businesses.
- Brand Dilution: When customers are unable to distinguish between genuine and counterfeit products, loyalty weakens and market share declines.
Counterfeiting is more than simply an annoyance; it is a growing issue with economic, managerial, and reputability risks. Businesses must invest in protective solutions to ensure their future.
Emerging Trends in Counterfeit Prevention

Counterfeiting is a chronic problem in a variety of businesses, including designer goods and drugs. As counterfeiters employ more complex strategies, the need for enhanced detection tools and stronger legal frameworks has become vital. Here are some of the latest developments in preventing counterfeit items:
1. Digital Counterfeit Detection Technologies
Technological innovation is changing the way we tackle counterfeit products, providing new techniques for spotting and avoiding fraud. Here are a few:
- AI-Powered Detection: Artificial intelligence examines product photos, packaging, and other data to detect counterfeit products. Machine learning algorithms may detect small inconsistencies that humans may overlook.
- Blockchain: By securely monitoring a product's origin and route, this technology assures authenticity, making product verification and fraud prevention easier.
- IoT and Smart Tags: RFID labels and QR codes provide real-time tracking and rapid authentication at the point of sale or delivery.
2. Consumer Awareness Campaigns
Consumer education about counterfeit hazards is a critical component of fraud prevention. Many customers still lack the expertise required to discern between genuine items and counterfeits. Here are the approaches:
- Increased Awareness Programs: Brands are increasing efforts to educate customers about the hazards of counterfeit products, focussing on typical indicators such as poor quality, packaging defects, and unusually cheap costs.
- Training on Identifying Fakes: Training programs provide customers with practical tools for identifying counterfeits. For example, educational information on product labelling, package characteristics, and security measures might assist people in identifying anomalies.
- Using Social Media: Influencers and advertisers are sharing ideas on how to recognise phoney items and prevent fraud on platforms such as Instagram and Facebook.
3. Legislation and Enforcement
Governments throughout the world are strengthening legislation to combat imitations, but implementation differs by location. Let us have a closer look at several regulations:
- US Intellectual Property Guidelines: The United States has severe patent rules that allow firms to pursue administrative or judicial action against fraudsters, with penalties ranging from fines to jail.
- EU Harmonised Regulations: Europe's consistent legal framework promotes cross-border collaboration and strengthens brand protection across member states.
- Asia's Diverse Regulatory Approaches: Enforcement in Asia varies, with some nations having robust systems and others struggling. Different regions necessitate unique tactics.
- Civil vs. Criminal Enforcement: Depending on the scenario and available resources, brands might choose between civil litigation for damages and criminal prosecutions for serious crimes.
While duplication remains an ongoing threat, novel innovations and a growing focus on customer outreach and oversight provide hope for a safer future. Brands and regulators are collaborating to create a multifaceted strategy to stop the spread of counterfeit items while safeguarding people as well as companies.
Implementing Effective Anti-Counterfeiting Strategies

Adopting an integration of technology and practices is critical for protecting items from manufacturing to the point of sale. The following are significant tactics for combating fraud:
1. Supply Chain Transparency.
- Fairness across the supply chain is crucial in preventing counterfeiting. When firms follow the passage of items from manufacture to sale, they may more easily verify authenticity and identify possible dangers.
- Real-time product tracking enables visibility at all stages of the supply chain. This makes it easier to discover abnormalities.
- Logistics monitoring technologies can warn organisations about unauthorised distribution or diversion of items.
- A comprehensive audit trail helps to prove the origin and course of a product. It helps boost consumer confidence.
2. Authentication Technologies
Several credentials are available to assist businesses and customers in determining the legitimacy of items. Brands can use innovative technology to ensure that only authentic items enter the market.
- Unique Codes and QR Codes: Scannable code formats or unique serial numbers on items allow customers and companies to rapidly check authenticity, lowering the possibility of imitation.
- Holograms and smart labels: These security elements are difficult to counterfeit and serve as a visual sign of validity.
- Blockchain: By using blockchain, businesses may build an immutable and transparent record of the product's path from manufacturing to sale.
3. Consumer Engagement:
Involving customers in the battle against counterfeiting enables them to protect themselves from fraud. Here are some fundamental approaches to empower consumers:
- QR codes on packaging may be used to easily verify products using smartphones.
- Provide explicit directions for authenticating items using labels, QR codes, or websites.
- Raise customer knowledge of counterfeit threats by urging them to thoroughly inspect product specifications before purchasing.
Businesses may take the initiative to safeguard their goods and clientele against piracy through the utilisation of robust supplier transparency, contemporary verification technologies, and customer loyalty.
How Acviss Prevents Counterfeit Products
Acviss is an international leader in anti-counterfeit technology, offering innovative solutions to safeguard business products and brand integrity. Acviss uses cutting-edge technology to ensure that clients receive only genuine things, minimising the impact of counterfeit goods on consumer trust and earnings.
Here's what sets Acviss apart:
- Non-Cloneable Labels: Each product is issued a unique, tamper-proof identity that prevents cloning or replication, confirming its validity.
- Track & Trace Technology: This technology enables real-time tracking and monitoring across the whole supply chain, assuring complete transparency and eliminating counterfeiting at any step.
- Blockchain Integration: Acviss leverages blockchain to keep immutable records of each goods journey, ensuring that the product's authenticity can be verified at any time.
- User-Friendly Verification: Consumers may quickly check product authenticity by scanning QR codes with their smartphones, providing peace of mind in a quick and simple process.
Acviss has helped various companies across sectors effectively combat counterfeiting.
Here is a real-life story:
Case Study: Gainz4Ever
Industry: Health Supplements
Challenges Faced:
- Counterfeiting damaging customer trust.
- Unauthorised reselling and unaccounted sales returns.
- Lack of cost-effective anti-counterfeit measures.
- Limited consumer engagement and transparency.
Acviss Solution:
- Product Authentication: Deployed 50,000+ non-cloneable labels across all products for instant verification.
- Transparency: Integrated a web-based authentication system with Shopify, ensuring seamless inventory and user management.
- Customer Engagement: Enabled easy product authentication for consumers via QR code scans, improving trust and satisfaction.
Results:
- Counterfeits are eliminated across online and offline channels.
- Enhanced customer trust, driving a significant rise in sales.
- The fully operational solution was deployed in just 14 days.
Gainz4Ever’s success story demonstrates how Acviss empowers brands to safeguard their products and strengthen consumer trust in highly competitive markets.
Conclusion
The emergence of counterfeit items is becoming a growing worry for brands. Businesses must address this issue immediately. As counterfeiters become more proficient, the hazards to brand reputation and customer trust grow dramatically. Brands that fail to take preventive steps risk losing not just money but also client loyalty, as counterfeit items reduce the perceived value of legitimate products.
Fortunately, improvements in AI and technology give effective answers to this problem. Companies can protect their items against duplication through the adoption of technologies such as blockchain for product identification, AI-powered tracking systems, and digital watermarking. Moving forward, it is a no-brainer for companies to adopt these inventive ideas, as they present a clear route to retaining brand integrity and ensuring sustainability in a highly competitive environment.
Want to know more about anti-counterfeiting technologies? Get in touch with us today and secure your brand and products across online and offline channels.
